How Childhood Emotional Neglect Can Make You an Avoidant Adult
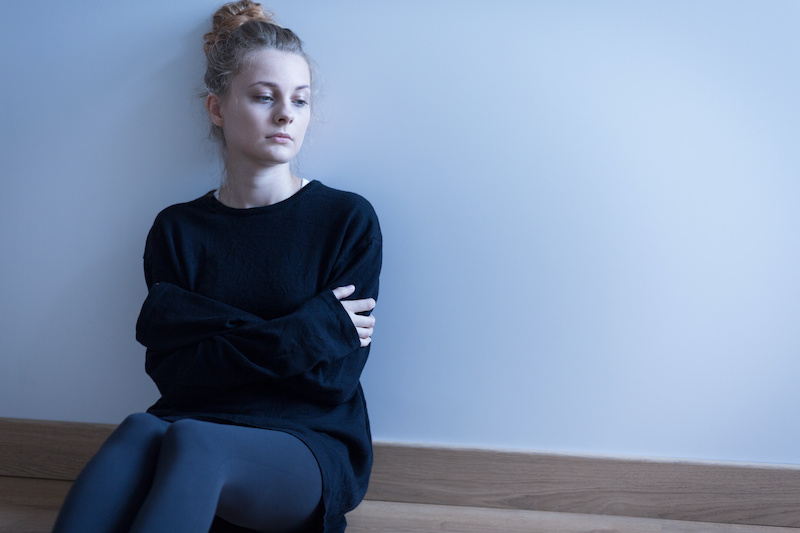

You shy away from the limelight. You stay out of trouble. You prefer to stay out of the way. You try not to make waves.
Of all of the kinds of anxiety people can experience, avoidance is probably one of the least studied and least talked about. I think that’s probably because avoidant folks are quiet. They do stay out of the way and they do not tend to make waves.
But, the reality is, avoidance is a serious problem to live with. Take a look at the characteristics of avoidance below. These are some of the symptoms listed in the DSM (The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders) to identify Avoidant Personality Disorder. Please note that these are not a full description of Avoidant Personality. Do not attempt to use these symptoms to diagnose yourself or someone else. Only a licensed mental health professional is qualified to make a diagnosis.
- Secretly feeling inferior to others, and struggling with shame
- Reluctance to pursue goals, take risks or meet new people
- High sensitivity to criticism, and fear of rejection
- Assuming that others see you in a negative light
- Trying not to get too close to people
- You suspect that you enjoy things less than other people do
- Often having anxiety in social situations
You may read through the list above and feel that you are reading about yourself. Even if you answer yes to only some of the items above, it means that you may have an “avoidant style.”
Many people are living their lives with Avoidant Personality disorder. And many, many more folks have an avoidant style. Most avoidant folks fight their own private battles on their own, secretly and quietly.
It is very possible to suffer silently with an intense fear of rejection, closeness, or social situations but still soldier on, essentially unimpaired on the outside, but miserable on the inside.
Now let’s talk about you. Do you see yourself in this description of avoidance? We will talk more about avoidance in a moment. But first, we must discuss Childhood Emotional Neglect (CEN). Because I have seen a remarkable connection between Childhood Emotional Neglect and avoidant tendencies in adults.
Childhood Emotional Neglect (CEN): When your parents fail to respond enough to your emotions and emotional needs.
What happens to a child whose parents too seldom say, “What’s wrong?” and then listen with care to their answer. How does it affect a child to have parents who are blind to what they are feeling? Parents who, through probably no fault of their own, fail to offer emotional support, or fail to truly see the child for who she is?
Childhood Emotional Neglect teaches you, the child, to avoid feeling, expressing, and needing. You are learning to avoid the very thing that makes you the most real and the most human: your emotions.
When you grow up this way, you grow up feeling invisible, and believing that your emotions and emotional needs are irrelevant. You grow up feeling that your emotional needs should not exist and are a sign of weakness. You grow up to feel ashamed that you have feelings and needs at all.
CEN is a breeding ground for shame, low self-worth, and yes, avoidance.
Five Important Points About Avoidance
- Avoidance is actually nothing more than a coping mechanism. If you avoid something that scares you, you do not have to deal with it. That feels like success.
- You developed this coping mechanism for a reason in your childhood. You needed it, and it probably, in some way, served you well in your childhood home. It may have been the only coping mechanism you could learn if no one was helping you learn other, more effective ways of coping.
- When you use avoidance enough as a way to cope, it eventually becomes your “signature move.” It becomes a solution that you go to over and over again. It becomes your style.
- Avoidance feeds fear. The more you avoid what you fear, the more you fear it. Then the more you avoid it. And so on and so on and so on, around and around it goes in an endless circle, growing ever larger.
- All of the symptoms of avoidance you saw at the beginning of this article have one common denominator that drives them. It’s a feeling and also a belief. It is this: a deep, powerful feeling that you are not as valid as everyone else. Somehow, on some level, you just don’t matter as much. This is one of the prime consequences of Childhood Emotional Neglect. (I call it The Fatal Flaw.)
It is very difficult to take on challenges in life when you don’t believe in yourself. It’s hard to be vulnerable in relationships when you don’t feel on equal footing with the other person. It’s hard to put yourself out there when you feel so secretly flawed.
This is why you must not let avoidance run your life. You must turn around and face it. Not later. Not tomorrow. But now.
You Can Become Less Avoidant
- Answer this question for yourself: What did you need to avoid in your childhood home?
- Accept that your avoidance is a coping mechanism that can be replaced by far better, healthier coping skills.
- Start observing yourself. Make it your mission to notice every time you avoid something. Start a list, and record every incident. Awareness is a vital first step.
- Look through the list, and notice the themes. Is there a trend toward avoiding social situations? Risks? Goals? Feelings? Needs?
- Start, little by little, one-step-at-a-time, facing things. How pervasive is your avoidance? If it is everywhere of everything, I urge you to seek a therapist’s help. If you have success on your own, be persistent. Don’t give up, no matter how hard it gets.
- Learn more about Childhood Emotional Neglect. To find out whether CEN was a part of your childhood, I invite you to take the Emotional Neglect Questionnaire. It’s free.
The more you face things, the less scary they become, and the easier they become to face again, and the more you face. And so on and so on and so on, around and around it goes in an endless circle, growing ever larger.
But this circle is a healthy, strong one that is a reversal of the circle of avoidance that began in your childhood. This circle will take you somewhere healthy and positive and good.
To learn more about Childhood Emotional Neglect, how it happens, and how it causes avoidance, see the book, Running on Empty: Overcome Your Childhood Emotional Neglect.
Three Amazing Ways You Can Re-Parent Yourself
The First Way – Compassionate Responsibility
In my office, I’ve heard from clients stories of broken phones, punched walls, and even bent steering wheels. All in the name of anger.
At themselves.
For making a mistake.
What You Didn’t Get
When a parent sits down with a child who has behaved badly, used poor judgment, or made a mistake, and says, “Let’s figure out what happened,” that parent is teaching her (or his) child Compassionate Responsibility.
 But many parents don’t know that it’s their job to teach their child how to process a mistake; how to sift through what happened and sort out what part of it belongs to circumstances, and what part belongs to the child. What can we learn from this? What should you do differently next time?
But many parents don’t know that it’s their job to teach their child how to process a mistake; how to sift through what happened and sort out what part of it belongs to circumstances, and what part belongs to the child. What can we learn from this? What should you do differently next time?
There is a balance between all of these factors which must be understood. The parent holds the child accountable, but also helps him (or her) understand himself and have compassion for himself and his mistake.
What To Give Yourself
If your parents were too hard or too easy on you for mistakes, or failed to notice them at all, it’s not too late for you now. You can learn Compassionate Responsibility today. Follow these steps when you make a mistake.
- Remind yourself that you are human, and humans are not perfect. Everyone makes mistakes.
- Think through the situation. What went wrong? Are there things you should have known, or realized, or thought about? Those are the parts that you own. Those are where you’ll find the lessons for you to take away from this. Take note of what you can learn, and etch it into your memory. This can be the growth that results from your error.
- Have compassion for your humanness: Your age, your stress level, and the many factors that contributed to this mistake.
- Vow that next time you’ll use your new knowledge to do better. Then put this behind you.
The Second Way – Self-Discipline
We are not born with the ability to manage our impulses. Self-discipline is not something that you should expect yourself to have automatically. Self-discipline is learned. In childhood.
What You Didn’t Get
When parents have rules, and enforce them firmly and with love, they are naturally teaching their childre how to do this for themselves. Do your homework before you go out to play. Fill the dishwasher, even though you don’t want to. You are not allowed to have a second dessert. Balanced, fair requirements enforced with care by your parents teach you how, years later, to do this for yourself.
What To Give Yourself
If you struggle with self-discipline more than most other people, it does not mean that you are weak-willed or less strong than others. It only means that you didn’t get to learn some important things in childhood. Never fear, you can learn them now. Follow these steps.
- Stop blaming yourself for your struggles with self-discipline. When you accuse yourself of being weak or deficient, you make it harder to get a foothold on making yourself do things you don’t want to do, and on stopping yourself from doing things that you shouldn’t do.
- If you are too hard on yourself at times, chances are high that you also, at other times, go too far in the opposite direction. Do you sometimes let yourself off the hook when you don’t follow your own rules? This, too, is damaging.
- Use the Compassionate Responsibility skills you are building by applying them each time you fall down on self-discipline.
The Third Way – Learn to Love the Real You
We all learn to love ourselves in childhood; that is, when things go well. When we feel our parents’ love for us, it becomes our own love for ourselves, and we carry that forward through adulthood.
What You Didn’t Get
We tend to assume that if our parents loved us, that’s enough. But it isn’t necessarily, at all. There are many different ways for a parent to love a child. There’s the universal type of parental love: “Of course, I love you. You’re my child.” Then there’s real, substantive, meaningful parental love. This is the love of a parent who really watches the child, really sees and knows the child, and really loves the person for who he or she truly, deeply is.
What to Give Yourself
Most people receive at least some of the first type of love. Far fewer receive the second type. Do you feel that your parents truly know the real you? Do they love you for who you are? Do you love yourself this way? Truly and deeply? If you sense something is missing in your love for yourself, it may be because you didn’t receive enough genuine, deeply felt love from your parents. But it’s not too late for you to get it. You can give it to yourself.
- Accept that it’s not your fault that your parents couldn’t love you in the way you needed.
- Start paying more attention to yourself. Who are you? What do you love and hate, like and dislike, care about, feel, think? These are the aspects of you that make you who you are.
- Pay special attention to what’s good about you. Make a list and keep adding to it. Are you a loyal friend? A hard worker? Dependable? Caring? Honest? Write down everything that occurs to you, even if it’s very small. Re-read the list often. Take these qualities in and own them. They are you.
Growing up with mostly Type 1 Love has a far more serious impact than you think. It’s highly correlated to not learning Compassionate Responsibility and self-discipline. If you see yourself in this article, read more at EmotionalNeglect.com and the book, Running on Empty.
Your Parents: 10 Signs You May Need Some Healthy Boundaries
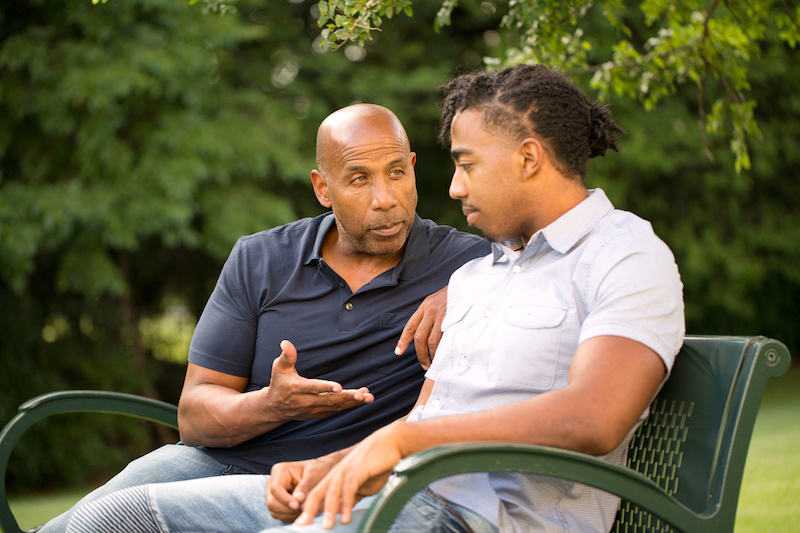

Few would disagree that parents have the most difficult job in the world. And the huge majority of parents are doing the very best they can for their children.
As much empathy as I have for parents (being one myself), today I will be talking with all who are on the other side of the fence: those of you who are grown up now and are feeling that your relationship with your parents is challenging in some way.
There are indeed an infinite amount of ways that a parent/child relationship can go wrong. Many are subtle or confusing and can leave all parties feeling burdened or hurt.
Especially if you know that your parents love you, you may end up baffled about your relationship with them, and wondering what is wrong.
6 Common Ways Adults Struggle With Their Parents
- You may feel guilty for not wanting to spend more time with them
- You may feel very loving toward them one minute, and angry the next
- You may look forward to seeing them, and then feel let down or disappointed when you’re actually with them
- You may find yourself snapping at them and confused about why you’re doing it
- You may get physically ill when you see them
- You may harbor anger at them, and feel there’s no reason for it
How does this happen? Why does this relationship have to be so complicated? Why can’t we just love our parents unconditionally?
Of course, there can be endless different explanations for any of these problems. But for most people, the answer lies somewhere in the area of what psychologists call individuation.
What is Individuation?
Individuation is the natural, healthy process of the child becoming increasingly separate from the parent by developing his or her own personality, interests, and life apart from the parent.
Individuation usually starts around age 13 but can be as early as 11 or as late as 16. Behaviors we think of as “teenage rebellion” are actually attempts to separate. Talking back, breaking rules, disagreeing, refusing to spend time with the family; all are ways of saying, and feeling, “I’m me, and I make my own decisions.”
Individuation is indeed a delicate process, and it doesn’t always go smoothly. When it doesn’t, and also goes unresolved, it can create a stressful or painful relationship between parent and adult child.
4 Ways Individuation Can Go Awry
- The parent does not know that the child’s individuation is natural and healthy, and discourages it. This parent may feel hurt by the child’s separation, or even be angered by it, making the child feel guilty for developing normally.
- The parent wants the child to stay close to take care of the parent’s needs, so actively discourages the child from separating.
- The parent is uncomfortable with the child’s needs, and so encourages the child to be excessively independent at too early an age (an example of Childhood Emotional Neglect or CEN).
- The child is held back from healthy individuation by some conflict or issue of his or her own, like anxiety, depression, a physical or medical ailment, or guilt.
When your adolescence gets off track in any of these ways, a price is paid by both you and your parents. Much later, when you’re trying to live your adult life, you may sadly find yourself feeling burdened, pained, or held back by your parents. On top of that, you might feel guilty for feeling that way.
So now the big question.
How Do You Know if You Need Some Healthy Distance From Your Parents?
- Do you feel held back from growing, developing, or moving forward in your life by your parents?
- Is your relationship with your parents negatively affecting how you parent your own children?
- Are you afraid of surpassing your parents? Would they be hurt or upset if you become more successful in life than they?
- Are you plagued with guilt when it comes to your parents?
- Are your parents manipulating you in any way?
- Are their needs coming before your own (the exception is if they are elderly or ill)?
- Were/are your parents abusive to you in any way, however subtle?
- Have you tried to talk with them and solve things, to no avail?
- Do you feel that your parents don’t really know you?
- Do your parents stir up trouble in your life?
If you answered yes to one or more of these questions, and you also feel burdened by your relationship with your parents, it may be a sign that you need some distance to maximize your own personal growth and health.
You and Your Parents
Yes, parenting truly is the hardest job in the world. But parents are meant to launch you, not limit you. If your individuation didn’t happen properly through your adolescence, you may need to work at separating from your parents now in order to have the healthy, strong, independent life that you are meant to live.
So what does distancing mean when it comes to parents? It doesn’t mean moving farther away. It doesn’t mean being less kind or loving toward them. It doesn’t necessarily mean doing anything drastically different. In fact, distance can be achieved by changing yourself and your own internal response to what happens between you. I know this sounds difficult and complicated.
Guilt is, for many, built into the adult separation process, unfortunately. So separating from your parents may be no less painful now, as an adult, than it was when you were an adolescent. But the good news is, you are grown up. You’re developed. You’re stronger. Now you can better understand what’s wrong.
To learn more about how even loving parents can have a blind spot to their child’s feelings, disrupting individuation, and to find out what you can do about it now, see the books Running on Empty: Overcome Your Childhood Emotional Neglect and Running On Empty No More: Transform Your Relationships With Your Partner, Your Parents & Your Children.
A version of this article was originally published on Psychcentral.com. It has been republished here with the permission of the author and Psychcentral.
4 Ways You Can Use Your Anger to Make Yourself More Powerful

Of all human emotions, the one that people struggle with the most is anger. That’s understandable!
After all, it’s the emotion with the most potential to get us into trouble. It can be exquisitely uncomfortable, and it’s the most difficult to control.
Many people find it easier to push anger down altogether (or suppress it) to avoid discomfort and conflict and to stay out of trouble.
Some wear anger like armor in hopes it will protect them from being hurt or mistreated.
Others go back and forth between pushing it down and erupting. In fact, these two things go together. The more you suppress your anger, the more intense it will be when it finally erupts.
If you were raised by parents who had low tolerance for your feelings (Childhood Emotional Neglect, or CEN), then you may be all too good at pushing your anger away; suppressing it and repressing it so that you don’t even have to feel it.
In fact, you may – especially if you have CEN – be so uncomfortable with the A-Word that you can’t even say it.
I’m frustrated
I’m annoyed
I’m anxious
you may say instead of, I’m angry.
If you’re not comfortable with your anger, you’re more likely to misread and mislabel it as something milder or more diffuse.
“Isn’t stopping yourself from feeling angry a good skill to have?” you may be wondering.
The answer is actually NO.
Research has shown how very important anger is to living a healthy life.
4 Reasons to Make Friends With Your Anger
- Anger is a beautiful motivator
Aarts et al. (2010) found that people who were shown a picture of an angry face were more driven to obtain an object that they were shown later. Anger is like a driver that pushes you to strive for what you want or need. Anger carries with it the message, “Act!”
Example Without Anger: Alana was getting weary of being overlooked at work. She was well-known to be skilled and reliable, and yet she was repeatedly passed over for promotion to manager. Silently she watched younger, less experienced employees move past her, one by one.
Example With Anger: Alana became angry when a less-experienced colleague was promoted. “I deserve an explanation for this. I have to get myself promoted or leave the company,” she realized. The next day she walked into her supervisor’s office and asked why she was passed over. She was promised the next promotion slot.
2. Anger can make your relationship better and stronger
Anger, when used appropriately, can be very helpful in communication:
Baumeister et al. (1990) found that hiding anger in intimate relationships can be detrimental. When you hide your anger from your partner, you’re bypassing an important message that he or she may very much need to hear.
Of course, it’s important to take great care in how you express your anger. Try your best to calibrate it to the situation and express it with as much compassion for your partner as you can.
Example Without Anger: Lance was tired of his wife Joanne’s clutter. She kept, it seemed to Lance, virtually everything. There were stacks of newspapers on the dining room table, five pairs of sneakers of various ages in their closet, and a roomful of clothes that their children had outgrown. Lance wanted that room for an office. “I’ll never get that room,” he thought resignedly. All this time Joanne had no idea that there was a problem.
Example With Anger: Lance was fed up with the clutter. He told Joanne that it was making him feel stressed and unhappy, and also angry at her. After several heated discussions, Joanne removed her personal clutter from the spare room so that Lance could make it his office. They made a truce to try to meet each other in the middle.
3. Anger can help you better understand yourself
Anger can provide insight into ourselves if we allow it.
Kassinove et al. (1997) asked a large sample of people how recent outbursts of anger had affected them. Fifty-five percent said that getting angry had led to a positive outcome. Many respondents said that the anger episode had provided them with some insight into their own faults.
Anger can help you see yourself more clearly. And it can motivate self-change.
Example Without Anger: Joanne was surprised when Lance told her how angry her clutter was making him. “That’s too bad, you’ll just have to deal with it,” she said dully while exiting the room. She promptly put it out of her mind because she didn’t want to think about it.
Example With Anger: “That’s too bad, you’ll just have to deal with it,” Joanne fired back immediately. She stormed out of the room and slammed the bedroom door. Sitting on her bed she felt enraged and criticized.
The next day Joanne woke up with a different perspective on the conflict. She looked around and saw her home as though through Lance’s eyes. She realized that she felt criticized by Lance’s request. “I need to get better at taking criticism,” she thought.
4. Anger helps you negotiate
Anger can help you get what you want.
In a study of negotiation by Van Kleef et al. (2002), people made larger concessions and fewer demands of participants who were angry than ones who were not angry.
Anger makes you more powerful, especially when it’s justified and expressed with thought and care. Lets revisit Alana, who needed to have a difficult conversation with her supervisor.
Example Without Anger: Alana walked timidly into her supervisor’s office. After chatting about the weather, she said casually, “So what do I need to do to get promoted?” Her boss answered her question and went on with her day.
Example With Anger: Alana knew she was angry and that she needed to manage her anger when talking with her boss if she wanted to be effective. She walked into her boss’s office and said, “I need to talk to you about something important.” Alana explained how upset she was by her co-worker’s promotion. Her boss explained that the promoted co-worker was an excellent employee. This made Alana even angrier. She pushed, “Yes, he’s really good. But so am I, and I have more experience and excellent skills,” she stated clearly. Her boss paused, surprised at Alana’s persistence. “You’re right,” she said. Her boss then promised Alana the next available promotion.
If you grew up emotionally ignored or in an environment that did not have the room or tolerance for you to get angry (CEN), some small part of your brain probably screams “STOP!” as soon as you get an inkling of anger. The reality is that it’s not easy to turn that around.
But you can do it. Start thinking of anger as a helpful emotion, not something to avoid. Pay attention to your anger, and try to notice when you’re feeling it. Stop saying “STOP!” to your anger. Instead, listen to your anger’s message, consciously manage your angry feeling, and let your anger motivate and energize you.
Anger, when properly managed and expressed, is power.
So when you suppress your anger, you’re suppressing your power.
And why would you do that?
To learn more about how Childhood Emotional Neglect makes you unaware of your feelings of anger see the book, Running On Empty: Overcome Your Childhood Emotional Neglect.
Everyday Struggle of a Notorious People Pleaser
Guest post by Joanna Rogowska:
I like to reward myself at the end of the week with a delicious meal with friends. It’s my weekly treat. I also like to check out new restaurants. So when my two good friends Lucy and Jane suggested meeting in our favorite burger place, I proposed a new Japanese restaurant instead. I had heard good things about the food and what caught my interest was their new interactive ordering system with overhead projection technology.
I’d read that each table in the restaurant was equipped with a built-in tablet. You could select your virtual tablecloth, explore the menu, project a picture of the meal onto your table, and of course, also order your food. I love new technological gadgets!
When we arrived, I fell in love with this place straight away – beautiful and authentic Japanese decor, lotus flowers, cherry blossoms, bamboo benches, and high-tech tables. A fantastic combination of traditional and modern Japan.
Lucy and I started ordering the meal, getting all excited about it. It was a really cool experience to be able to project the picture of each meal onto the plate in front of you. We played around with changing virtual table cloths, debating which one we were going to choose for our table. I realized that I was feeling something.
Playful, connected, excited, and happy.
As we were exploring the technological possibilities at our table, Jane suddenly called the waiter over and asked for a paper menu. “I really don’t know how to make this digital stuff work!” she told us. “It’s really not intuitive and annoying. I prefer a normal menu.”
Suddenly my pleasant feelings disappeared and a big sense of heaviness took their place. I suddenly felt overwhelmingly bad. I looked at Lucy and she seemed to continue enjoying looking through the menu and ordering her meal. But for me, as soon as Jane asked for a paper menu, I stopped enjoying the evening.
In the past, before learning how to master my emotions, I would have sat miserably throughout the rest of the meal feeling confused and simply “bad.” I would have let this ruin my evening. Now I knew better, and it was time to check in with my feelings to investigate what was going on. So I tuned in to my emotions.
Annoyed, Irritable.
Makes sense. I was looking forward to dinner today and suddenly I was not able to enjoy it. My intention was to relax and have a good time and now I was far from that, so I felt angry. But the big question was, why was I not enjoying the evening? I knew I had to dig deeper to find the right feelings.
Insecure, awkward, guilty, and ashamed.
As soon as I identified shame, I felt a sense of relief. It made so much sense for two reasons. First of all, I know I am a compulsive people pleaser. I tend to always put other people’s needs in front of my own. I cannot have a good time if I see that my friends are not enjoying themselves. So seeing Jane not enjoying the technology made me feel guilty for suggesting to go there.
But I knew there was more behind this feeling so I dug deeper. I had known that Jane was not a big fan of technology, yet I had still suggested this restaurant. How could I have been so inconsiderate? All I could think of was the fact that I was stupid because I couldn’t even pick the right restaurant for my friends…
Going through these feelings in my head brought me a sense of relief. I was feeling less and less overwhelmed and uncomfortable and beginning to feel some new feelings.
Clear, confident, and capable.
My feelings reminded me that the well-being of my friends was important to me. So I thanked my feelings for drawing my attention to the situation. I accepted my feelings and released them. I also accepted that my inner critic blew the situation slightly out of proportion, as things were actually going well. It was difficult to accept that, but it felt liberating to do so.
Finally, I reassured myself that Jane, having received her paper menu, was enjoying selecting her meal in a more traditional way and no one was thinking any less of me for choosing this location.
I once again felt what I had felt at the beginning of the evening.
Connected, joyful, and excited.
The dinner turned out to be fantastic. We had a great time and we were pleased with the new discovery we made and the food we ate.
How quickly I could have let my emotions take over and ruin my evening if I hadn’t paid attention to them and made the effort to understand them. That was a reminder to me once again of how important it is for me to observe myself and try to understand my feelings.
The author, Joanna Rogowska, is a researcher for FeelingMagnets.com. Feeling Magnets are a helpful tool to get you more in touch with your emotions and learn how to use them.
To learn more about how to recognize, use, and express your emotions see the book, Running on Empty.
9 Things the Emotionally Attuned Parent Says to Their Child

As we all swim together through the murky Sea of Parenting, I offer you some clear answers: three goals to keep in your mind at all times, and exactly how to achieve them.
If you’ve made many parenting mistakes, rest assured: You Are Not Alone.
Let’s face it, parenting is hard. For most of us, doing it right means facing our own demons. Because no one is exposed to our flaws, blind spots, or unresolved issues as much as the children who depend on us.
Unfortunately, all of those unresolved problems transfer automatically from ourselves to our children, unless we make a conscious effort to stop them. This is made more or less difficult for us parents by our own childhoods.
The Subtle But Dramatic Impact of Childhood Emotional Neglect
If you grew up with parents who subtly discouraged or discounted your feelings (Childhood Emotional Neglect), for example, then you’ll have a natural inclination, outside of your awareness, to do the same with your children. This is why Childhood Emotional Neglect, or CEN, is so rampant in today’s world. It transfers, unchecked and unnoticed, from one generation to the next.
This natural transfer process is aided by one simple fact: In today’s world, we are all focused primarily on how our children behave. We don’t want them to get in trouble at school or irritate others, right?
Although it’s very reasonable to assume that teaching a child to behave takes care of the emotional part, nothing could be further from the truth. In reality, it all happens in reverse. Our children’s behavior is driven by their emotions. So the best way to help our children to behave is to teach them how to manage their feelings.
The Keys to Emotional Intelligence
There’s another key reason to focus more on emotions with our children. In the last ten years, a large body of research has found that kids who are good at recognizing, tolerating, expressing, and managing emotions in themselves and others (high emotional intelligence) are more successful academically, make better leaders, and enjoy greater career success as adults.
I know what you’re thinking: “OK, so it’s important. How do you do it? Behavior is at least concrete and visible, but feelings are hidden, messy, and confusing. What’s a parent to do?”
So let’s get down to brass tacks. As we all swim together through the murky Sea of Parenting, I offer you some clear answers: three goals to keep in mind at all times, and exactly how to achieve them.
The Three Goals of the Emotionally Attuned Parent
- Your child feels a part of something. He knows he’s not alone. You’re always on his team.
- Your child knows that whatever she feels, it’s OK, and it matters to you. She will be held accountable for her behavior, but not for her emotions.
- Your child learns how to tolerate, manage, and express his feelings.
Any parent who accomplishes these skills well enough is raising an emotionally healthy child and an emotionally intelligent child. You don’t have to do it perfectly. You just have to do it well enough.
9 Things the Emotionally Attuned Parent Says to Their Child
| WHAT WE ALL TEND TO SAY | WHAT THE IDEAL PARENT SAYS |
| Stop Crying | Why are you crying? |
| Let me know when you’re done with your fit | That’s OK. Get it all out. Then we’ll talk. |
| Alright, enough! I’m done with this. | Let’s take a break so we can both calm down. |
| Fix the attitude! | You sound angry or upset. Are you? |
| You need to think before you act! | How’d this go wrong? Let’s think it through. |
| Go to your room until you can behave better. | I see you’re angry. Is it because…? |
| OK, OK, stop crying now so we can go in the store. | Look at me. Take a deep breath. Let’s count to five. |
| There’s nothing to be nervous about. | Everyone gets nervous. It’s OK. Let’s talk. |
| Don’t talk to me with that tone. | Try saying that again, but nicer so I can hear it. |
All children have very intense emotions, but they do not have the skills to manage them. When we are frustrated or overwhelmed by their expression of feeling, it becomes very difficult for us parents to manage what we’re feeling so that we can respond the right way to what they’re feeling.
No one sets out purposely to shame their child for having emotions. But the way we respond can easily, in very subtle ways, communicate to a child that he shouldn’t be feeling what he’s feeling.
Keep in mind that virtually all children have heard everything in the first column many times, and it’s OK. It will only cause damage (Childhood Emotional Neglect) if the child receives the subtle, unstated messages listed below too frequently:
* Your feelings are excessive.
* Your feeling is wrong.
* I don’t want to know what you’re feeling.
* Your feelings are an inconvenience for me.
* You need to deal with this alone.
* I don’t care what you feel; I only care about your behavior.
If you wince while you read those messages above, don’t despair! It’s not your fault. You’re simply doing what human beings do, and responding to your children as you were responded to as a child. Be assured, it is never too late to start responding differently.
Try using the “Ideal Parent” responses above as regularly as possible, keeping in mind that you will never be perfect because no one is. Watch and see if over time your child starts to respond to you differently. Watch to see how her behavior changes as she learns how to manage her own feelings.
To learn more about emotionally attuned parenting, how to raise your child with high Emotional Intelligence, and how to prevent CEN from being passed down, see the book, Running On Empty No More: Transform Your Relationships With Your Partner, Your Parents & Your Children. To learn much more about how CEN happens and how to heal it, see the book, Running on Empty.
To find out if you grew up with CEN Take The Emotional Neglect Test. it’s free.
A version of this article was originally posted on psychcentral.com. It has been updated and republished here with the permission of the author and psychcentral.
Got Issues? It’s All Your Parents’ Fault
Everything that’s wrong in your life is the fault of your parents. Whatever your struggles, your mistakes and your pain, you are not to blame. You are an innocent victim of those who raised you.
At least that’s the way some folks interpret my definition of Childhood Emotional Neglect (CEN).
The definition of CEN: A parent’s failure to respond enough to the child’s emotional needs. People who grow up this way go forward into adulthood out of touch with their own emotions, feeling empty, alone and disconnected, and are baffled about what is wrong with them.
Here’s a comment that was posted on Ten Steps to Learn Self-Discipline:
Are you saying that when a parent fails to teach their children this skill well enough, that parent is guilty of Childhood Emotional Neglect? This article was insulting.
I’ve received many such comments. They point to one of the biggest barriers I have encountered in my efforts to bring the concept of Childhood Emotional Neglect to more people: the discomfort of blaming the parents.
Despite the overwhelming body of research proving it, many people strongly resist the fact that their parents’ treatment of them in childhood had a profound effect upon who they are as adults. It is uncomfortable to blame our parents for the problems and issues that we experience in adulthood. It feels like letting ourselves off the hook. Some people consider it “whining.”Continue reading
Robin Williams and Childhood Emotional Neglect
 Since Robin Williams’ sad and shocking suicide on August 11, friends, family, fellow stars, and even reporters have offered multiple explanations for the virtually inexplicable:
Since Robin Williams’ sad and shocking suicide on August 11, friends, family, fellow stars, and even reporters have offered multiple explanations for the virtually inexplicable:
Why did he do it?
Some of the many possible factors which have been proposed are depression, alcohol, drugs, and Parkinsons Disease. But I see another potential factor which is never mentioned by anyone. A factor which falls between the cracks just as its sufferers do: Childhood Emotional Neglect (CEN).Continue reading
Do You Have Alexithymia?
Alexithymia: Difficulty in experiencing, expressing and describing emotions.
Every day I hear from folks who have just realized that they grew up with Childhood Emotional Neglect (CEN). Often they say, “Finally I understand what’s wrong with me!” Many describe a huge weight lifted from their shoulders.
It is a wonderful thing to finally understand yourself in a new and useful way. Unfortunately, however, it is not enough. Step 1 is seeing and understanding the problem. Step 2 is healing the problem. Continue reading
Take the Childhood Emotional Neglect Test
During twenty years of practicing psychology, I started to see an invisible force from childhood which weighs upon people as adults. It’s a “non-event” which is unnoticeable and unmemorable and yet leaves a profound mark upon the child that endures throughout adulthood. It’s Childhood Emotional Neglect (CEN).
CEN is a parent’s failure to respond enough to a child’s emotional needs.
This failure to respond can masquerade as loving parent behavior. It can happen in families which are seemingly healthy and fine. And it can be overshadowed by more obvious child mistreatment or abuse. In any case, it goes unseen and unnoticed while it does its silent damage to people’s lives.
Many people have found answers to problems that have baffled them throughout their lives, by recognizing that CEN is the cause. But because CEN is so difficult to see or remember, it can be very hard to identify whether you are living your adult life in its grip. I’ve devised the Emotional Neglect Questionnaire to help you discover whether you may have grown up this way.
I have found it very useful, but have not yet been able to establish reliability or normative data through research. So please know that, at this point, the ENQ is based upon clinical experience, and has not been scientifically studied yet.
Sign up to Take The Emotional Neglect Questionnaire
_________________________________________________________________________________
To learn more about CEN; how it happens, why it’s so invisible, and how to heal from it, visit EmotionalNeglect.com, or see Running on Empty: Overcome Your Childhood Emotional Neglect.



